As hardware interfaces evolve, the textbook definition of input devices often citing trackballs and light pens has become obsolete. This guide analyzes the modern Human Interface Device (HID) landscape, from high-polling gaming mice to spatial computing controllers, ensuring you understand the tools that truly define interaction today.
In modern computing, an input device is a transducer. Its primary role is to convert one form of energy kinetic (movement), acoustic (voice), or visual (gestures) into an electrical signal that the operating system can interpret.
What Are Input Devices?
An input device is a piece of hardware equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system, such as a computer or information appliance. These devices act as the bridge between the physical world and digital logic, translating human actions (like typing, gesturing, or speaking) into machine-readable code that the Operating System (OS) can process.
In the modern data processing cycle, input devices are the first step. Without them, a computer acts as a black box capable of processing but unable to receive instructions. While legacy definitions focused on simple text entry, modern input devices enable spatial awareness, biometric authentication, and haptic feedback.
Key Characteristics of Modern Input
- Connectivity: Shift from PS/2 and Serial ports to USB-C, Thunderbolt 4, and Bluetooth 5.3.
- Latency: Measured in milliseconds (ms), critical for gaming and real-time creation.
- Sensor Type: Evolution from mechanical balls to Optical Tracking, capacitive sensing, and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems).
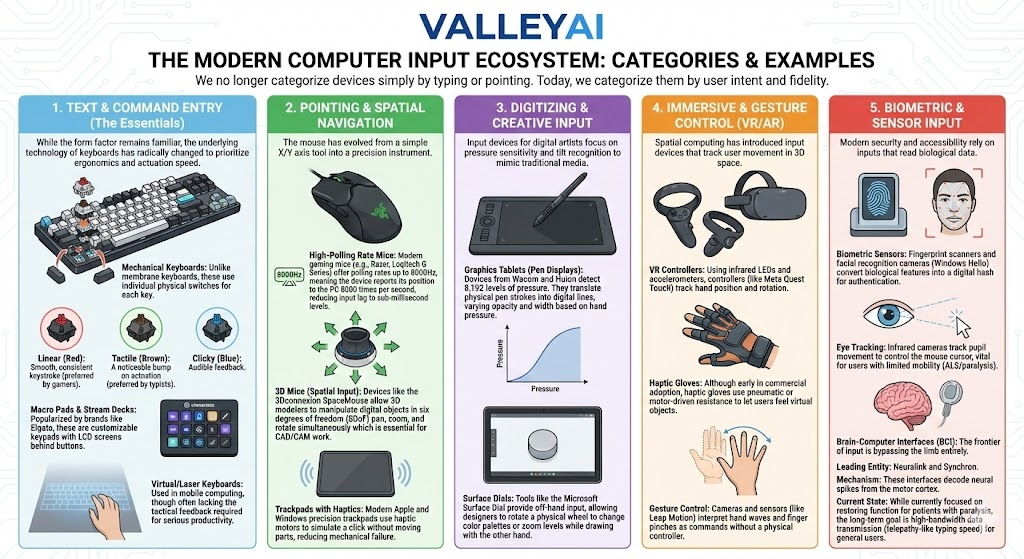
The Modern Computer Input Ecosystem: Categories & Examples
We no longer categorize devices simply by typing or pointing. Today, we categorize them by user intent and fidelity.
1. Text & Command Entry (The Essentials)
While the form factor remains familiar, the underlying technology of keyboards has radically changed to prioritize ergonomics and actuation speed.
- Mechanical Keyboards: Unlike membrane keyboards, these use individual physical switches for each key.
- Linear (Red): Smooth, consistent keystroke (preferred by gamers).
- Tactile (Brown): A noticeable bump on actuation (preferred by typists).
- Clicky (Blue): Audible feedback.
- Macro Pads & Stream Decks: Popularized by brands like Elgato, these are customizable keypads with LCD screens behind buttons. They allow users to trigger complex macros, launch apps, or control streaming software with a single press.
- Virtual/Laser Keyboards: Used in mobile computing, though often lacking the tactical feedback required for serious productivity.
2. Pointing And Spatial Navigation
The mouse has evolved from a simple X/Y axis tool into a precision instrument.
- High-Polling Rate Mice: Modern gaming mice (e.g., Razer, Logitech G Series) offer polling rates up to 8000Hz, meaning the device reports its position to the PC 8000 times per second, reducing input lag to sub-millisecond levels.
- 3D Mice (Spatial Input): Devices like the 3Dconnexion SpaceMouse allow 3D modelers to manipulate digital objects in six degrees of freedom (6DoF) pan, zoom, and rotate simultaneously which is essential for CAD/CAM work.
- Trackpads with Haptics: Modern Apple and Windows precision trackpads use haptic motors to simulate a click without moving parts, reducing mechanical failure.
3. Digitizing & Creative Input
Input devices for digital artists focus on pressure sensitivity and tilt recognition to mimic traditional media.
- Graphics Tablets (Pen Displays): Devices from Wacom and Huion detect 8,192 levels of pressure. They translate physical pen strokes into digital lines, varying opacity and width based on hand pressure.
- Surface Dials: Tools like the Microsoft Surface Dial provide off-hand input, allowing designers to rotate a physical wheel to change color palettes or zoom levels while drawing with the other hand.
4. Immersive & Gesture Control (VR/AR)
Spatial computing has introduced input devices that track user movement in 3D space.
- VR Controllers: Using infrared LEDs and accelerometers, controllers (like Meta Quest Touch) track hand position and rotation.
- Haptic Gloves: Although early in commercial adoption, haptic gloves use pneumatic or motor-driven resistance to let users feel virtual objects.
- Gesture Control: Cameras and sensors (like Leap Motion) interpret hand waves and finger pinches as commands without a physical controller.
5. Biometric & Sensor Input
Modern security and accessibility rely on inputs that read biological data.
- Biometric Sensors: Fingerprint scanners and facial recognition cameras (Windows Hello) convert biological features into a digital hash for authentication.
- Eye Tracking: Infrared cameras track pupil movement to control the mouse cursor, vital for users with limited mobility (ALS/paralysis).
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI)
The frontier of input is bypassing the limb entirely.
- Leading Entity: Neuralink and Synchron.
- Mechanism: These interfaces decode neural spikes from the motor cortex.
- Current State: While currently focused on restoring function for patients with paralysis, the long-term goal is high-bandwidth data transmission (telepathy-like typing speed) for general users.
Future Outlook: By 2030, we expect Hybrid Input Environments where eye-tracking selects an object, and a subtle neural command clicks it, eliminating the need for physical mouse movement entirely.
Technical Function: How Input Data is Processed
Input devices function by converting physical energy into electrical signals, which are then interrupted and processed by the CPU.
Understanding this workflow explains why lag occurs and how high-performance devices mitigate it.
- Transduction: The device captures a physical action (e.g., a key press closes a circuit).
- Encoding: The device’s internal controller converts this signal into a scan code or binary data packet.
- Transmission: The data travels via USB or Bluetooth to the computer’s I/O controller.
- Interrupt Request (IRQ): The I/O controller sends an interrupt signal to the CPU, halting its current task to handle the input.
- Driver Interpretation: The OS driver (often a generic HID driver or proprietary software like Logitech G Hub) translates the raw data into a command (e.g., Type letter ‘A’).
Expert Insight: Modern High-Polling devices overwhelm older CPUs by sending too many interrupts. Windows 11 has optimized the input stack to handle 8000Hz polling rates, but legacy OS versions may stutter under the load.
Comparison: Input vs Output Devices
The primary difference is the direction of data flow: Input devices send data to the processor, while output devices receive processed data from the processor to display or actuate.
| Feature | Input Devices | Output Devices |
|---|---|---|
| Direction of Flow | User $\rightarrow$ Computer | Computer $\rightarrow$ User |
| Primary Function | Instruction & Data Entry | Reproduction & Display |
| Data Type | Raw Signals (Keystrokes, Scans) | Processed Info (Images, Sound) |
| Modern Examples | VR Controller, Stream Deck, Mic | 4K Monitor, Haptic Feedback, 3D Printer |
| Interaction | Active (User initiates) | Passive (User perceives) |
User Guide: Choosing the Right Input Devices
Selecting the correct peripherals depends heavily on your primary use case. Below is a breakdown of essential features based on user intent.
1. For Competitive Gamers
- Priority: Low Latency and Precision.
- Recommended Specs:
- Mouse: Optical sensor, <1ms response time, lightweight (<60g).
- Keyboard: Mechanical switches (Red/Silver linear) with “N-Key Rollover” (ghosting protection).
- Connection: Wired USB-C or 2.4GHz Wireless (Bluetooth is generally too slow for competitive play).
2. For Creative Professionals (Designers/3D Artists)
- Priority: Ergonomics and Granular Control.
- Recommended Specs:
- Tablet: High pressure sensitivity (4096+ levels) and tilt support.
- 3D Navigation: 6DoF controller (3Dconnexion) to reduce wrist strain from repetitive orbiting.
- Display: Color-accurate monitors with built-in KVM switches.
3. For Productivity & Remote Work
- Priority: Comfort and Multitasking.
- Recommended Specs:
- Keyboard: Ergonomic split designs or silent tactile switches (Brown) to reduce office noise.
- Mouse: Vertical mouse to prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
- Extras: High-quality webcam and dedicated microphone (MEMS) for Zoom/Teams clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions (Modern Input Devices Of Computer)
What are the most modern computer input devices?
Beyond standard keyboards, the most modern devices include Spatial Computing controllers (for Apple Vision Pro/Meta Quest), Haptic Gloves, Stream Decks for content creation, and Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) which are currently in experimental phases for accessibility.
How do VR controllers work as input devices?
VR controllers utilize a technology called 6DoF (Six Degrees of Freedom). They use a combination of internal gyroscopes/accelerometers and external LED tracking (monitored by headset cameras) to transmit the exact position (X, Y, Z coordinates) and rotation (pitch, yaw, roll) of your hand to the computer in real-time.
What is a Stream Deck used for?
A Stream Deck is a customizable control pad used primarily by streamers and power users. Each key is an LCD screen that can be programmed to perform specific actions such as switching camera angles, muting microphones, launching apps, or posting tweets automating workflows that usually require complex keyboard shortcuts.
Are haptic gloves commercially available for PC?
Yes, but they are primarily niche enterprise or enthusiast products. Companies like bHaptics and Manus produce gloves that offer tactile feedback for VR training and simulation. However, consumer-level support in standard PC games is still limited compared to enterprise applications.
How do biometric sensors provide input to a computer?
Biometric sensors (fingerprint/iris scanners) capture a high-resolution image of a biological feature. This input is not stored as an image but is converted into a mathematical representation (a hash). The computer compares this input hash against a stored hash to authorize access, acting as a security key input.
Kaleem
My name is Kaleem and i am a computer science graduate with 5+ years of experience in Computer science, AI, tech, and web innovation. I founded ValleyAI.net to simplify AI, internet, and computer topics also focus on building useful utility tools. My clear, hands-on content is trusted by 5K+ monthly readers worldwide.