What is an output device let cover first fundamentals. At its core, a computer is a data processing factory. But that processing is useless if the machine cannot communicate the results back to you.
An output device is any piece of computer hardware that converts information into a human-perceptible form or into a physical machine-readable form. It bridges the gap between digital binary code (0s and 1s) and the physical world.
While traditional definitions focus on seeing (monitors) or hearing (speakers), the 2026 standard for Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) includes devices that let you feel (haptics) and inhabit (spatial computing).
The Soft vs Hard Copy Distinction
- Soft Copy Output: Temporary, digital output. Examples: A document on an OLED screen, spatial audio from headphones, or a vibration from a haptic engine.
- Hard Copy Output: Permanent, physical output. Examples: A printed contract, a 3D printed prototype, or a bioprinted tissue scaffold.
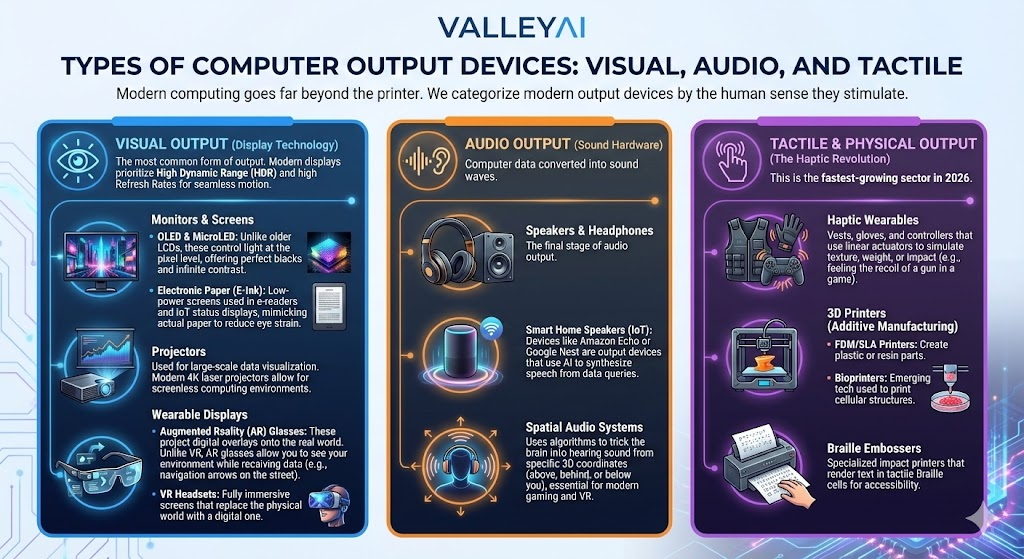
Types of Output Devices: Visual, Audio, and Tactile
Modern computing goes far beyond the printer. We categorize modern output devices by the human sense they stimulate.
Visual Output (Display Technology)
The most common form of output. Modern displays prioritize High Dynamic Range (HDR) and high Refresh Rates for seamless motion.
- Monitors & Screens:
- OLED & MicroLED: Unlike older LCDs, these control light at the pixel level, offering perfect blacks and infinite contrast.
- Electronic Paper (E-Ink): Low-power screens used in e-readers and IoT status displays, mimicking actual paper to reduce eye strain.
- Projectors:
- Used for large-scale data visualization. Modern 4K laser projectors allow for screenless computing environments.
- Wearable Displays:
- Augmented Reality (AR) Glasses: These project digital overlays onto the real world. Unlike VR, AR glasses allow you to see your environment while receiving data (e.g., navigation arrows on the street).
- VR Headsets: Fully immersive screens that replace the physical world with a digital one.
Engineer’s Note on Refresh Rates: For gaming performance, a 60Hz monitor is no longer the standard. Competitive players look for 144Hz to 360Hz displays. This reduces motion blur, allowing the user to see the output frame immediately after the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) renders it.
Audio Output (Sound Hardware)
Computer data converted into sound waves.
- Speakers & Headphones: The final stage of audio output.
- Smart Home Speakers (IoT): Devices like Amazon Echo or Google Nest are output devices that use AI to synthesize speech from data queries.
- Spatial Audio Systems: Uses algorithms to trick the brain into hearing sound from specific 3D coordinates (above, behind, or below you), essential for modern gaming and VR.
Tactile & Physical Output (The Haptic Revolution)
This is the fastest-growing sector in 2026.
- Haptic Wearables: Vests, gloves, and controllers that use linear actuators to simulate texture, weight, or impact (e.g., feeling the recoil of a gun in a game).
- 3D Printers (Additive Manufacturing):
- FDM/SLA Printers: Create plastic or resin parts.
- Bioprinters: Emerging tech used to print cellular structures.
- Braille Embossers: Specialized impact printers that render text in tactile Braille cells for accessibility.
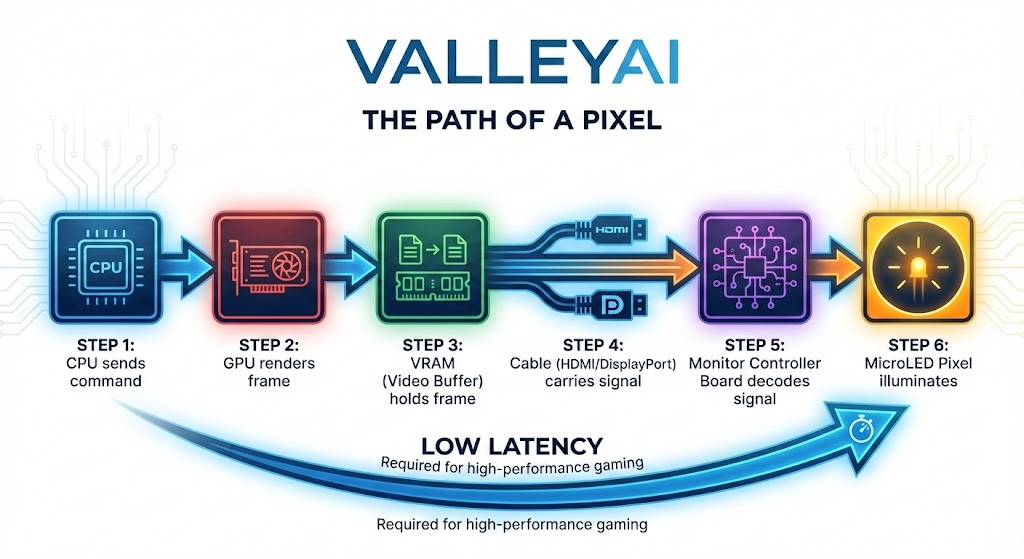
Deep Dive: How Data Flows (CPU to Output)
For the technical user: How does a string of code become a picture on your screen?
The journey from the Central Processing Unit (CPU) to the output device involves complex conversion and buffering.
The Mechanism of Action
- Processing: The CPU (or GPU) calculates the data and sends a digital signal.
- The Buffer: Data is temporarily stored in a frame buffer (for video) or audio buffer to prevent stuttering.
- The Driver: The Operating System uses a device driver (software) to translate the OS instructions into a language the specific hardware understands.
- Conversion (DAC): Most output is analog (light and sound). A Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) transforms binary data into varying electrical voltages.
- Example: In a speaker, the DAC turns digital audio files into voltage fluctuations that vibrate the speaker cone.
- Perception: The hardware activates (pixels light up, motors spin, nozzles spray) to present the data.
Visual Concept: The Data Flow Diagram
Input vs. Output Devices: The Comparison
Understanding the difference between output and input devices is vital for troubleshooting and system architecture.
| Feature | Input Devices | Output Devices | Hybrid (I/O) Devices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Sends data TO the CPU. | Receives data FROM the CPU. | Both sends and receives. |
| User Interaction | User controls the computer. | Computer informs the user. | Interactive loop. |
| Signal Flow | Human/Physical $\rightarrow$ Digital | Digital $\rightarrow$ Human/Physical | Bidirectional |
| Classic Examples | Keyboard, Mouse, Microphone | Monitor, Printer, Speakers | Touchscreens, Headsets w/ Mic |
| Modern Examples | LiDAR Scanners, Biometric Sensors | Haptic Suits, AR Glasses | IoT Smart Hubs, VR Controllers |
Pro Tip: Touchscreens are the most common source of confusion. They are technically two devices layered together: a display panel (Output) and a digitizer layer (Input).
Future And Emerging Output Technologies
To differentiate from legacy guides, we must look at where wearable technology and IoT are taking us.
The Internet of Things (IoT)
Output is no longer tethered to a desk. Smart light bulbs (Hue) are output devices they change color based on digital data (weather reports or email notifications). Smart thermostats adjust physical temperature as a form of output.
High-Fidelity Haptics
We are moving from simple rumble packs to skin-stretch feedback. New controllers simulate the tension of a bowstring or the texture of sand. This is crucial for training simulations (medical/military) and immersive gaming performance.
Direct Retinal Projection
Instead of looking at a screen, future AR glasses use low-power lasers to paint images directly onto the user’s retina, eliminating the need for a physical display panel and offering infinite depth of focus.
Why Output Devices Matter (Value Proposition)
Why invest in high-quality output hardware?
- Accessibility: Specialized output devices (Screen readers, Braille displays) democratize technology, allowing users with visual or hearing impairments to interact with digital data effectively.
- Precision for Remote Work: High-resolution 4K/8K monitors allow video editors and architects to see details invisible on standard screens.
- Immersion: In entertainment, spatial audio and high refresh rate screens create a flow state, suspending disbelief and deepening the experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are smart home speakers considered output devices?
Yes, and no. The speaker component that plays music or voice responses is an output device. However, the microphone that listens to your command is an input device. Collectively, they are Hybrid I/O devices.
How does data travel from the CPU to an output device?
Data travels via the system bus to the specific controller (like a GPU or Sound Card). It is then converted from digital binary code into analog signals (for sound/legacy video) or specific digital protocols (like HDMI packets) that tell the hardware exactly how to behave.
What is the difference between soft copy and hard copy output?
Soft copy is intangible and temporary (what you see on a monitor or hear through speakers). Hard copy is tangible and permanent (a laser-printed document or a 3D-printed model).
How do AR glasses function as output hardware?
AR glasses receive video data from a processor (either built-in or tethered to a phone) and project light into waveguides in the lenses. This light enters your eye, overlaying digital graphics on top of your view of the real world.
Kaleem
My name is Kaleem and i am a computer science graduate with 5+ years of experience in Computer science, AI, tech, and web innovation. I founded ValleyAI.net to simplify AI, internet, and computer topics also focus on building useful utility tools. My clear, hands-on content is trusted by 5K+ monthly readers worldwide.