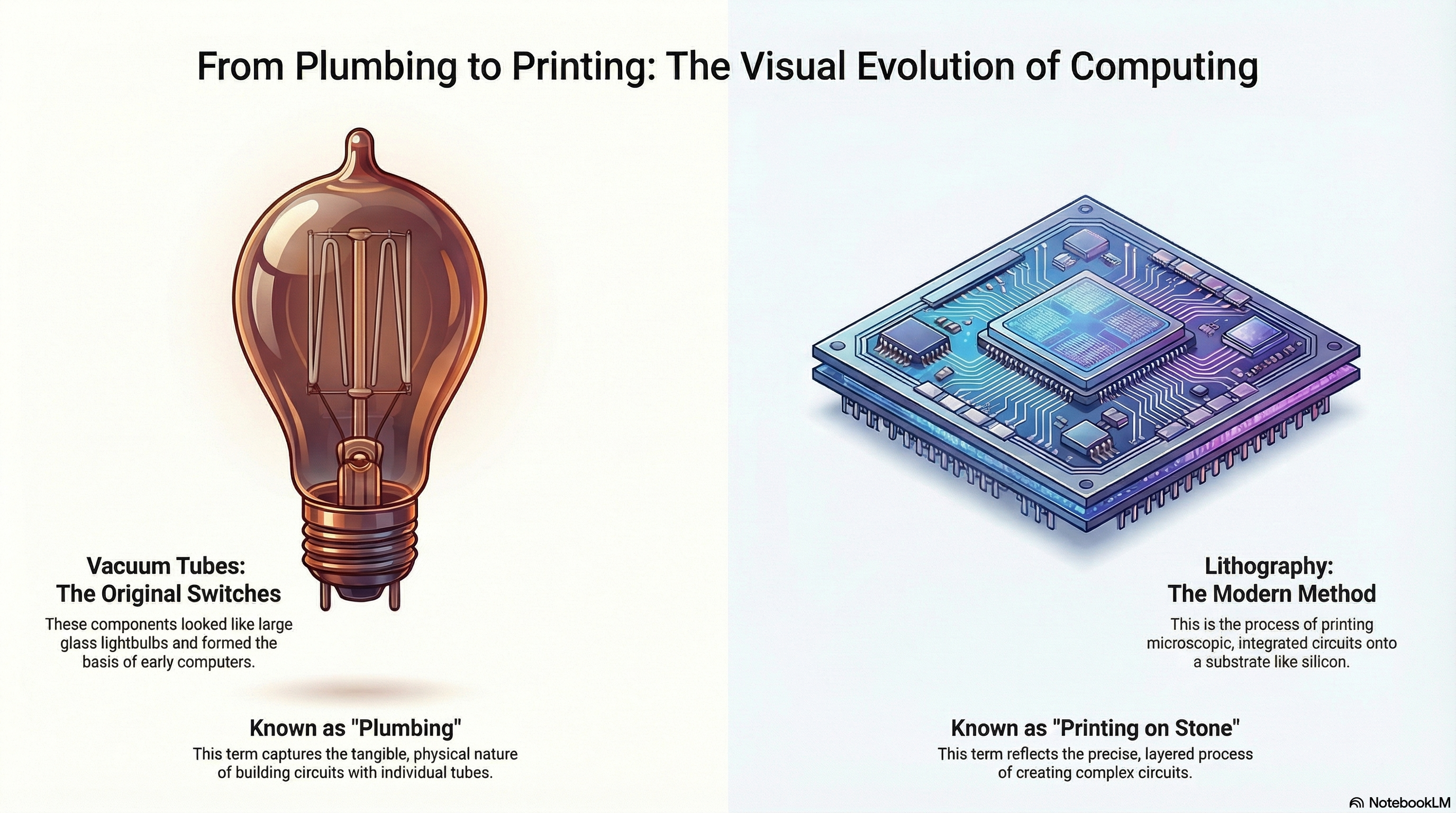
The answer to which invention allowed computers to become smaller is a two-part story. The fundamental shift occurred with the invention of the transistor in 1947, which replaced the bulky, hot vacuum tubes used in early mainframes.
However, while transistors made computers smaller (shrinking them from the size of a room to the size of a refrigerator), they did not make them portable. The invention that allowed for true miniaturization turning computers into desktops and eventually smartphones was the Integrated Circuit (IC), also known as the microchip.
To understand how we got from the 30-ton ENIAC to the smartphone in your pocket, you have to look beyond just the size of the components and understand the engineering nightmare known as the Tyranny of Numbers. So let discuss the Invention that Shrank the computer, from Transistors to Integrated Circuits.
The Bottleneck: Why Vacuum Tubes Kept Computers Huge
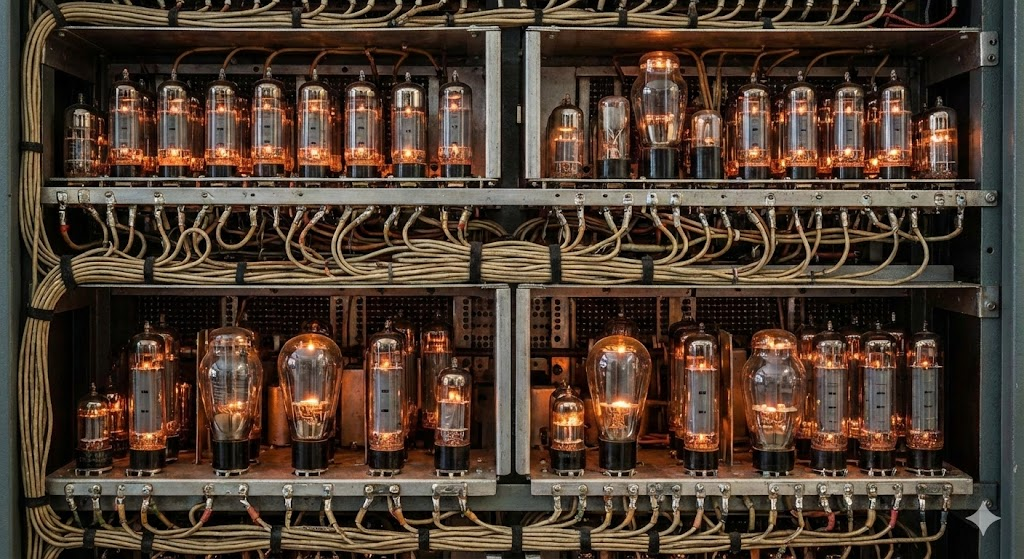
Early computers like the ENIAC (1945) were massive, occupying entire rooms and weighing roughly 30 tons. The primary reason for this bulk wasn’t just the size of the vacuum tubes themselves, but the environment they required.
Vacuum tubes functioned like lightbulbs. They generated immense heat and were prone to burning out. Because of this thermal output, engineers could not pack them tightly together. They had to be spaced out to prevent the machine from melting, requiring massive cooling systems and dedicated power plants.
The size of the computer was dictated by thermodynamics: if you needed more processing power, you needed more tubes, which meant you needed more physical space to dissipate the heat.
The First Leap: The Transistor (1947)
The first major breakthrough in size reduction was the transistor, invented by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley at Bell Labs.
The transistor performed the same function as a vacuum tube acting as a switch to control the flow of electricity (representing 1s and 0s) but it did so using solid semiconductor materials like germanium and later silicon.
This shift to solid-state electronics solved the immediate physical constraints:
- Size: A transistor was the size of a fingernail (and eventually much smaller), compared to a vacuum tube which was the size of a lightbulb.
- Heat: Transistors generated negligible heat, allowing them to be packed much closer together without requiring industrial air conditioning.
- Reliability: They didn’t burn out like bulbs.
However, the transistor introduced a new problem. Even though the components were small, early transistorized computers were still large, complex machines. The IBM 7090, a fully transistorized computer from 1959, still occupied a large room.
The problem was no longer the components; it was the wiring.
The True Miniaturization: The Integrated Circuit (1958)
By the late 1950s, engineers faced the Tyranny of Numbers. If a computer required 100,000 transistors, it also required hundreds of thousands of hand-soldered connections to wire them all together. This web of wires took up space, cost a fortune to assemble, and was a nightmare to troubleshoot.
The solution came from Jack Kilby (Texas Instruments) and Robert Noyce (Fairchild Semiconductor), who independently invented the Integrated Circuit (IC).
Their realization was brilliant in its simplicity: instead of manufacturing thousands of individual transistors and wiring them together, they could manufacture the transistors, the resistors, and the capacitors along with the connecting wiring all on a single block (monolith) of semiconductor material.
This shifted computer manufacturing from an assembly process (soldering parts together) to a printing process (photolithography).
- Eliminating Wires: Because the connections were printed microscopically within the silicon chip, the miles of copper wiring vanished.
- Exponential Scaling: This innovation allowed engineers to double the number of transistors on a chip roughly every two years, a phenomenon known as Moore’s Law.
The Final Leap: The Microprocessor (1971)
While the Integrated Circuit shrank computers from room-sized to fridge-sized, the invention that truly made them personal was the Microprocessor. Before 1971, the computers brain (CPU) was spread across several different chips and circuit boards.
In 1971, Intel engineers led by Ted Hoff and Federico Faggin unveiled the Intel 4004. This was the world’s first microprocessor a complete CPU on a single silicon chip no larger than a fingernail. By using LSI (Large Scale Integration) and later VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration), engineers could pack thousands, and eventually billions, of transistors onto one chip.
This was the Big Bang for size reduction. It turned the computer from an industrial machine costing $100,000 into a consumer appliance (like the Apple II or IBM PC) that could fit on a home desk.
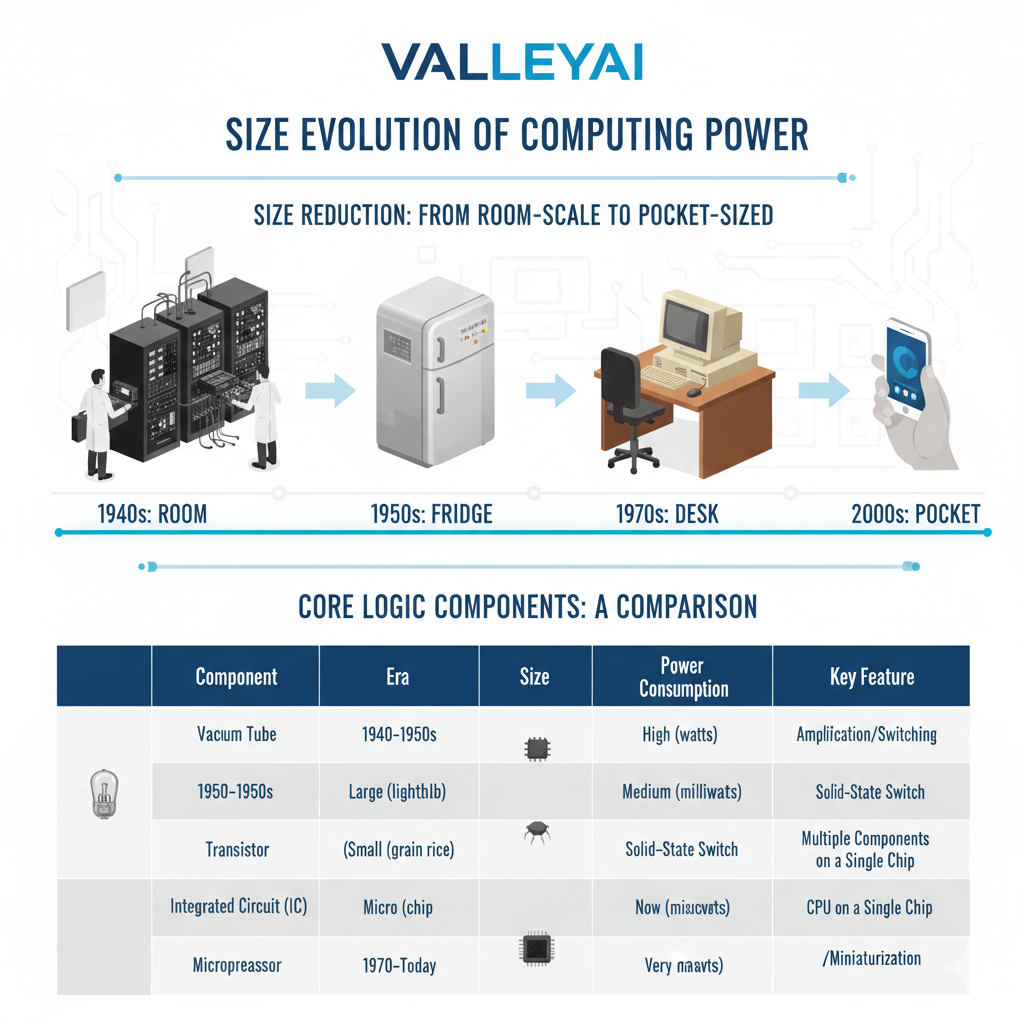
Summary of the Evolution
To visualize exactly how these inventions impacted size, look at the progression of the hardware:
- Vacuum Tube Era (1940s): Computers were Room-Sized. (Constraint: Heat and physical bulk of tubes).
- Discrete Transistor Era (1950s): Computers were Refrigerator-Sized. (Constraint: The volume of manual wiring required to connect thousands of individual transistors).
- Integrated Circuit And Microprocessor Era (1960s – Present): Computers became Desktop and Pocket-Sized. (Breakthrough: Printed circuits eliminated wires, allowing millions of components to fit on a chip the size of a coin).
Evolution of Size by Generation
Historians classify these size reductions into four distinct generations of computer:
- 1st Gen (Vacuum Tubes): Room-sized (e.g., ENIAC, 30 tons).
- 2nd Gen (Transistors): Refrigerator-sized mainframes (e.g., IBM 7090).
- 3rd Gen (Integrated Circuits): Filing-cabinet sized Minicomputers (e.g., PDP-8).
- 4th Gen (Microprocessors): Desktop and handheld Microcomputers (e.g., Apple II, Smartphones).
Common Misconceptions
When discussing this topic, terminology often gets confused. Here is the practical distinction:
- The Transistor is the ingredient. It is the switch that does the work.
- The Integrated Circuit is the recipe. It is the method of placing millions of those ingredients onto a single piece of silicon.
- The Microprocessor is a specific type of Integrated Circuit that functions as the brain (CPU) of the computer.
While the transistor was the scientific breakthrough that made electronic switching possible without heat, the Integrated Circuit was the manufacturing breakthrough that allowed computers to become small enough for personal use.
Final Words
The journey of computer miniaturization showcases remarkable human ingenuity. With the invention of microprocessors and integrated circuits, computers became more compact and efficient, paving the way for smaller, more powerful devices. As we move into the fifth generation, the focus shifts to gadgets that can understand natural languages and utilize artificial intelligence (AI).
These AI-driven systems and software present an exciting challenge for computer developers and programmers, further pushing the boundaries of technology and enhancing the brilliance of modern computers.
FAQs: Which Invention Allowed Computers To Become Smaller In size?
How did the transistor change computer design?
Transistors reduced the size and heat of computers, allowing engineers to build smaller, faster, and more reliable machines with better performance.
What came after transistors in computer development?
After transistors, integrated circuits (ICs) were invented. They allowed many transistors to fit on a small chip, leading to even smaller and more powerful computers.
Why are microprocessors important for small computers?
Microprocessors combine all core computing functions into a single chip. This allows desktops, laptops, and smartphones to be compact yet powerful.
Are modern computers still based on transistor technology?
Yes, modern computers use nano-scale transistors inside microchips. These tiny components power everything from tablets to supercomputers today.
What is the difference between a transistor and a microprocessor?
A transistor is a single electronic switch, while a microprocessor is a complex chip containing millions or billions of transistors acting as the computers entire brain.
Who invented the first microprocessor?
The first microprocessor, the Intel 4004, was invented in 1971 by a team at Intel led by Federico Faggin, Ted Hoff, and Stanley Mazor.
Related Topics For More Learning
- What is Moore’s Law? Understanding the rate of chip scaling.
- Analog vs. Digital Computers: How the method of calculation changed hardware needs.
- The History of the CPU: From the Intel 4004 to modern multi-core processors.
Kaleem
My name is Kaleem and i am a computer science graduate with 5+ years of experience in Computer science, AI, tech, and web innovation. I founded ValleyAI.net to simplify AI, internet, and computer topics also focus on building useful utility tools. My clear, hands-on content is trusted by 5K+ monthly readers worldwide.