The invention of IC chips was the pivotal moment that allowed computers to become smaller in size. These tiny marvels revolutionized the tech industry, making PCs more compact, faster, and more efficient. This change marked the dawn of a new era in technology, enabling significant advancements in various fields.
As a result, the cost of computers decreased tremendously over time, making them widely available to the masses. These compact devices paved the way for cloud computing and other smart things we rely on today.
This journey in the annals of innovation showcases how the development of IC chips not only made devices smaller but also revolutionized how we work and live. The increased power and efficiency of these computers have allowed for better decisions to be made faster and more accurately.
The tech industry has been shaped by this invention, which continues to be a pivotal force in making technology even more accessible and cost-effective.
Which Invention Allowed Computers To Become Smaller in Size?
The invention of the microchip and integrated circuit (IC) transformed computers, making them smaller and more efficient. By using semiconductor materials like silicon, these electronic devices replaced bulkier components, with the Silicon Transistor being a key factor in reducing computer size.
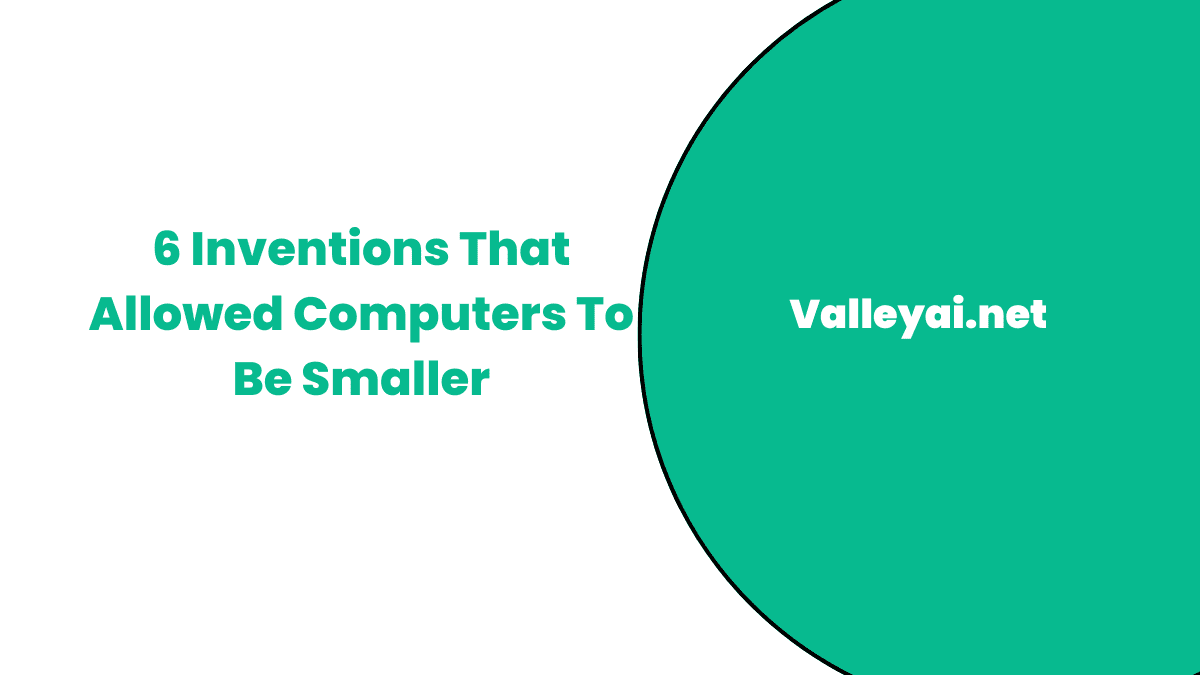
4 Different Key Inventions That Allowed Computers To Be Smaller
The Role of Transistors in Downsizing Computers
The discovery of transistors in 1947 by William Shockley, John Bardeen, and Walter Brattain was a game-changer in the world of computers. Unlike the bulky vacuum tubes used in first-generation computers like the ENIAC computer (which took up 1,800 square feet (167 square meters) of space with its 18,000 tubes), transistors offered a smaller, more reliable, and faster alternative.
This marked the transition to second-generation computers (1956-1963), where transistors replaced the less efficient and larger components found in early technology. These tiny semiconductor devices not only made computers smaller but also increased their speed and memory capacity.
By reducing the size of the CPU and replacing refrigerator-sized boxes with minuscule parts, transistors played a crucial role in the downsizing of computers. Their remarkable reduction in size and power consumption made them an essential tool in the miniaturization of devices. This invention led to computers becoming more dependable, powerful, and relatively cheap to produce on a large scale, further shaping the modern world of technology.
The Breakthrough of Integrated Circuits (ICs)
In the early 1960s, a major shift in computer technology began with the invention of integrated circuits (ICs) by scientists. These semiconductor chips allowed computers to become smaller, more reliable, and cheaper. Prior to ICs, second-generation computers used transistors, but the creation of ICs led to even more advancements. These IC chips contained multiple transistors on a single integrated circuit chip, allowing for less power consumption and enabling multiple applications to run simultaneously.
As a result, the size of third-generation computers (1964-1971) was dramatically reduced, with small-scale and medium-scale integrated circuits replacing larger, less efficient components. This meant computers could now be equipped with a keyboard and monitor, marking a significant leap in usability.
The integration of transistors on a single chip not only boosted computer power, but also lowered decreasing costs of production, making computers more accessible. This led to the normalization of the production procedure, saving space and other resources while enhancing computational speed.
The birth of ICs made computers more compact and advanced, allowing for more efficient operations in a smaller package. As technology continued to evolve, this innovation paved the way for modern computing, revolutionizing the world of electronics.
The Rise of the Microprocessor
The invention of microprocessors brought about a massive transformation in how computers were designed and used. These tiny chips became the brains of computers, replacing the older, bulky vacuum tubes and enabling a significant reduction in size without sacrificing performance.
With available power, these small processors fueled the development of mobile machines like laptops, tablets, and mobile phones, opening up uncharted potential for the evolution of technology. The shift allowed for faster, more efficient interaction with immaculate technology, pushing the boundaries of what computers could do.
Since 1971, the fourth-generation computers have relied on microprocessors, where a single chip handles all processing tasks. These chips, built on LSI (Large Scale Integration) and VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration), contain millions of transistors, making them incredibly compact and reliable. They also use less electricity and are reasonably priced, with some chips costing as little as $0.02.
The rapid, exponential growth in this field has made computers a household phenomenon, transitioning from our desks to our bags, pockets, and even fingers. These processors support powerful applications and modern programming languages like Visual Basic, C++, Java, and Python, marking a continuous leap in technology.
Key Microprocessor Developments Over the Decades
Over the years, microprocessors have gotten a lot better thanks to the prediction made by Moore’s Law. Here’s a list of the big moments in the life of microprocessors:
| Microprocessor | Year | Transistor Count |
| Intel 4004 | 1971 | 2,300 |
| Intel 8086 | 1978 | 29,000 |
| Intel 80386 | 1985 | 275,000 |
| Intel Pentium | 1993 | 3,100,000 |
| Intel Core i7 | 2008 | 731,000,000 |
| Intel Core i9 | 2020 | 10,300,000,000 |
Magnetic Storage to Solid-State Drives (SSDs): Shrinking Space, Expanding Potential
The shift from magnetic storage to solid-state drives (SSDs) played a key role in making smaller computers possible. Hard drives and storage devices evolved from their bulkier counterparts, leading to a remarkable reduction in size without sacrificing storage capacity.
Compact hard drives allowed users to store and access more data for complex tasks and projects, significantly improving efficiency and speed. As SSDs replaced traditional hard drives, the lack of moving parts further enhanced performance, contributing to the diminution of computer size and driving forward technological advancements.
Final Words
The journey of computer miniaturization showcases remarkable human ingenuity. With the invention of microprocessors, computers became more compact and efficient, paving the way for smaller, more powerful devices. As we move into the fifth generation, the focus shifts to gadgets that can understand natural languages and utilize artificial intelligence (AI).
These AI-driven systems and software present an exciting challenge for computer developers and programmers, further pushing the boundaries of technology and enhancing the brilliance of modern computers.
FAQs
Which invention allowed computers to become smaller in size?
The invention of the transistor made computers smaller by replacing large vacuum tubes. This helped computers become faster, more energy-efficient, and portable—laying the foundation for modern microchips.
How did the transistor change computer design?
Transistors reduced the size and heat of computers, allowing engineers to build smaller, faster, and more reliable machines with better performance.
What came after transistors in computer development?
After transistors, integrated circuits (ICs) were invented. They allowed many transistors to fit on a small chip, leading to even smaller and more powerful computers.
Why are microprocessors important for small computers?
Microprocessors combine all core computing functions into a single chip. This allows desktops, laptops, and smartphones to be compact yet powerful.
Are modern computers still based on transistor technology?
Yes, modern computers use nano-scale transistors inside microchips. These tiny components power everything from tablets to supercomputers today.
- SaaS Growth Strategies: A Complete Guide for Long-Term Success - May 18, 2025
- How Data Science Is Powering Business Decisions in 2025 - April 17, 2025
- The Future of Data-Driven Networking: Trends and Innovations - March 12, 2025